Five Ways AI and Robotics are Transforming Health Care

When one of the world’s leading consulting firms writes a lengthy piece on the promise of something, people tend to take notice. That’s precisely what happened in 2020 when McKinsey & Company penned a glowing executive brief titled, “Transforming healthcare with AI: The impact on the workforce and organizations.”
While that piece focused heavily on Europe, citing a joint report with the European Union’s EIT Health, what it also did was proclaim to the masses what those within the medtech industry already knew: The future of health care most definitely includes artificial intelligence (AI) and robotics. To expound on that point, we’ve curated a few noteworthy examples of exactly how this emerging technology is influencing and disrupting decades of status quo processes and procedures. Here are five ways AI and robotics are transforming health care.

AI can replicate the way our brains work for studying
To say the brain is complex would be the understatement of a lifetime, which is why researchers are still uncovering fascinating new nuggets of information about how it works hundreds of years after they started. But thanks to AI, they may be better equipped than ever to do so. For example, researchers are working on using AI and a machine learning-enabled mobile app to categorize a patient’s mental health status. Early results even indicate that the app performs as well or better than a human can.
In addition, AI is being used to build brain models, with those “virtual brains” producing patterns of neural activities not unlike what our real brains produce. From there, researchers can test theories and advance potentially groundbreaking discoveries.

AI is helping to catch diseases faster
We know in potentially fatal diseases like cancer that early detection saves lives. This fact has been proven by statistics like how screening has helped lower U.S. cervical cancer death rates by more than 50% in the last 30 years or how mammograms prevent 12,000 deaths from breast cancer annually. But doctors are now using AI to detect cancer even earlier—sometimes even before symptoms appear. One AI program was thought to have the capacity to reliably interpret mammograms and translate that data into diagnostic information at a speed 30 times faster than a human doctor. And when it came to precision, the program carried a 99% accuracy rate.
AI informs decision making
One of the most unique ways that AI disrupts the industry is through the accumulation of mass amounts of information, also known as big data. What the collection and analysis of big data does is augment the provider’s own intelligence and experience with gobs of additional examples. Using pattern recognition from similar cases, images and experiences, the provider can glean valuable insights used to inform next steps in the care continuum.

AI is being used in the operating room
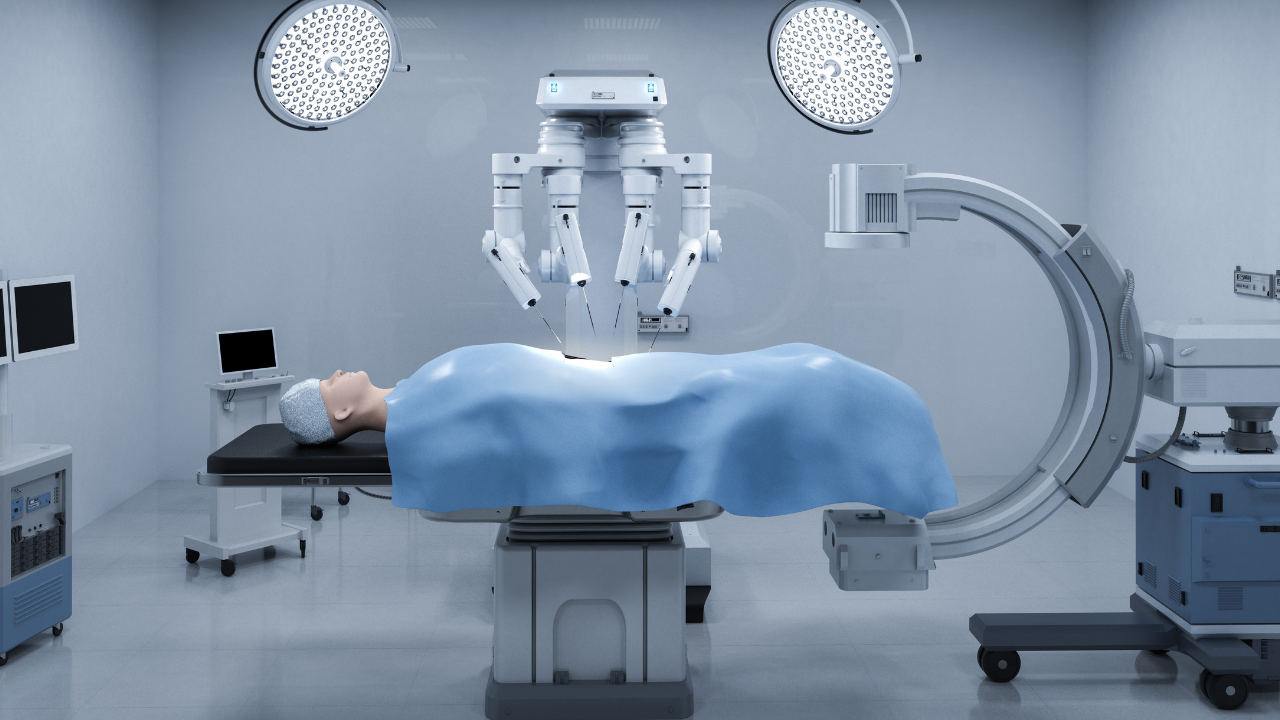
Perhaps the most well-known of the use cases involving AI and health care is robot-assisted surgery. As we alluded to, robotic surgery is not new—it’s actually been around for decades—but its importance to the field can’t be stressed enough. Robotic surgery enables surgeons to perform complex procedures with the type of precision and flexibility that wouldn’t be possible without the help of machines.
In most cases, these procedures include a robotic surgery system comprising a camera arm and mechanical arms that hold the surgical instruments. Meanwhile, the surgeon “operates” from a computer console at a nearby table. The benefits of robot-assisted surgery are numerous, including shorter hospital stays, less risk of infection, less blood loss and faster recovery. You might be surprised to learn that surgeons have been aided by AI and robotics in procedures involving a wide array of body parts, including the colon, heart, head, neck and spine.
AI is reducing providers’ administrative burden
Up until now, the examples we’ve included have directly impacted patients. But this one is for the hardworking providers who find themselves stressed, burnt out and buried under paperwork. Voice-first technology like smart speakers in clinics is proving to be valuable ways to reduce at least some of the administrative burden felt by providers and their staff. This technology is especially helpful in capturing conversations that are then translated into documentation for electronic health records.
That same technology can be useful for medical coding and billing, a process that is not only time-consuming and complex but one prone to mistakes from human data entry. The upshot of these changes is that by freeing up providers’ time from handling admin duties, that time can be used on patient needs. That’s what we call a win-win.
neuro42 is the next evolution of MRI and robotics
One area we didn’t mention above is how MRI intersects with AI and robotics. While there have certainly been some emerging technology developments within the field of imaging, we believe neuro42 is taking that tech to an entirely new level. Our goal is to develop the first-of-its-kind robotics-guided MRI that will allow physicians to diagnose brain injury in acute settings and treat neurological diseases intraoperatively under live imaging. We envision a future centered on neuro42 fusing MRI, AI and robotics, and we couldn’t be more excited to see how we’ll get there.

